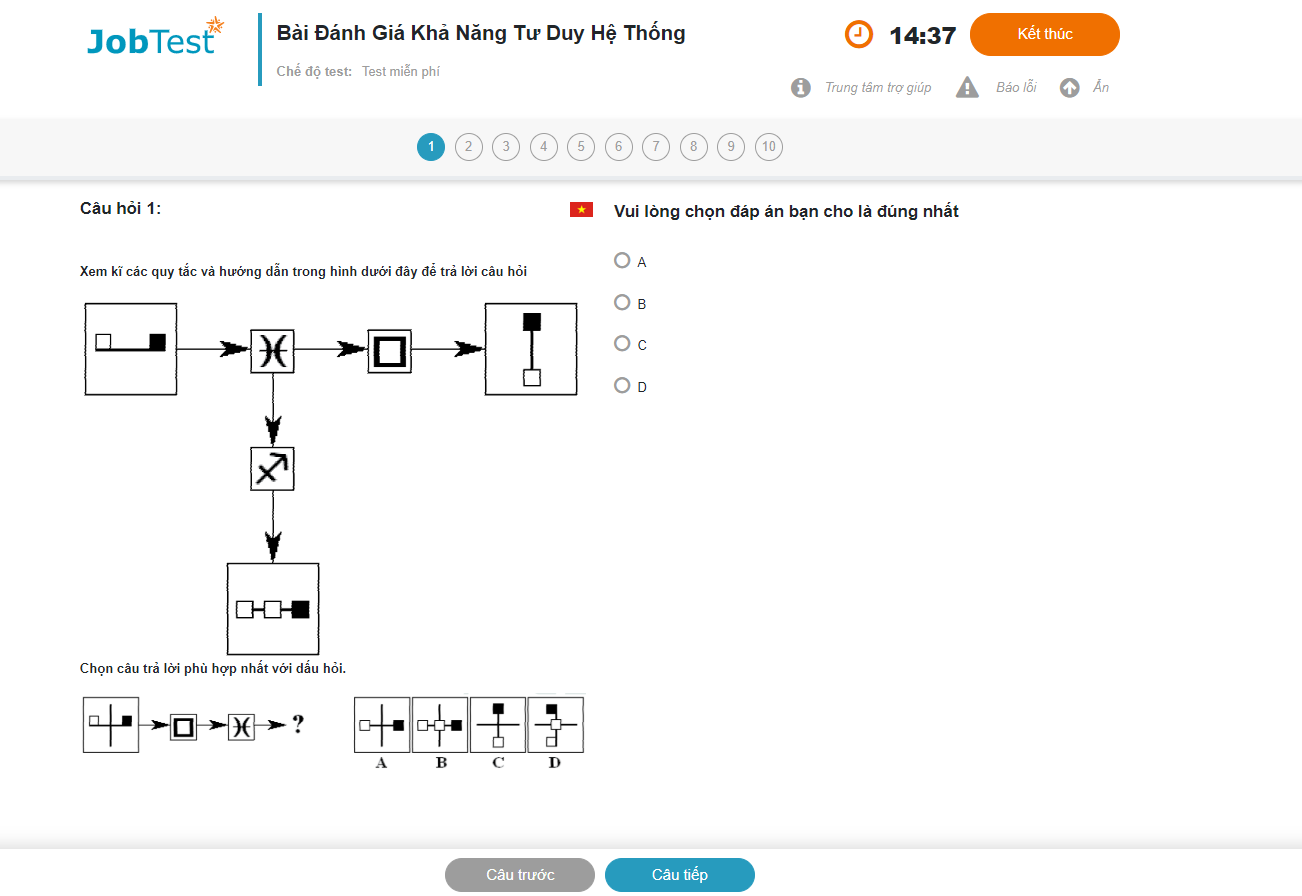
Diagrammatic Reasoning Tests Package
đ
210,000đ
- Think strategically and systematically about problems and developments within the relevant business field.
- Quickly analysize new information, communicate it to the overall scheme of things, and apply it to solve work-related problems.
- Effectively process and analysize new work-related data in a logical manner.

Diagrammatic Reasoning Tests Package
The assessment package includes a variety of tests. You can freely practice with a rich set of test questions, improve and properly evaluate your system thinking ability. The assessment package includes 9 topics for you to practice your Systems Thinking ability.
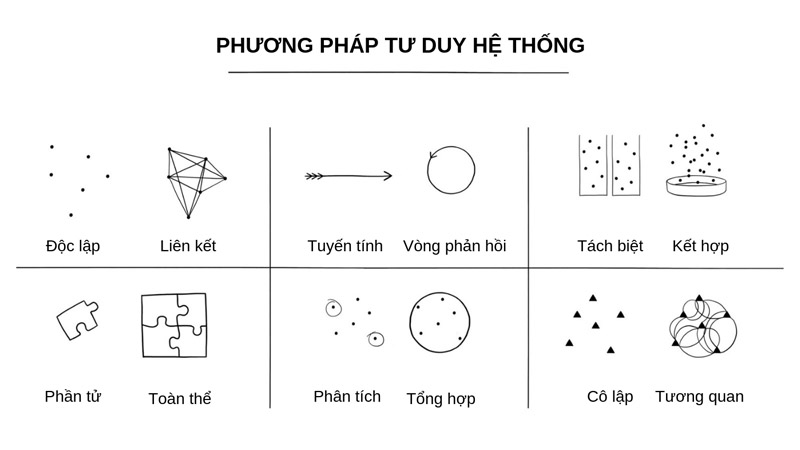
Components of Systems Thinking
Systems thinking can be likened to an important "weapon" when it comes to the most difficult problems in daily life and work. Systems thinking essentially emphasizes the relationships between the parts of a system. Systems thinking has practical value based on a solid theoretical foundation.

Systems thinking has four components:
- Model thinking: understanding problems through modeling.
- Correlational thinking: thinking is approached according to the systematic, correlated structure.
- Dynamic thinking thinks in terms of dynamic processes (delays, feedback loops, oscillations).
- Directing systems capabilities for the management of practice systems and control systems.

Model thinking
Instead of solving real problems, systems thinking models them. You will handle the problem according to the model. However, modeling thinking also includes the ability to build models. The model must be built, validated, and further developed. The ability to build models and analyze models depends in large part on the tools available to describe the model. The key to systems thinking is to choose an appropriate representation.

Relativistic thinking
If-then relations are the basic building blocks of the mind to understand things. The foundation of this way of thinking is to draw a precise line between cause and effect.
To explain a phenomenon you must find its "cause". Contrast this way of thinking in a cause-and-effect relationship, which can be called functional thinking or linear thinking. All in all, it's relational thinking.
Correlational thinking is a way of thinking that takes into account direct and indirect consequences. The network of causes and effects, the feedback process, develops into such structures over time.

Active thinking
Active thinking also means foreseeing future developments based on behavioral systems over time. A mere retrospective of past development is not enough for actual steering of the system - like whether you can trust a driver to just drive by looking in the rearview mirror to identify the driver. where do you go? Simulation models are useful or even necessary to project future developments, especially when reality emerges rather slowly.

Directing the system
In social systems it is often not possible to change the behavior of others directly. You can only change your own behavior. Likewise, in an economic system, producers usually do not control the market directly. Market activities are usually supply-side activities to appeal to a demand-side desire response

Why is systems thinking valuable?
Because it can help design-wise, prolong the solution of the problem. In the simplest sense, systems thinking provides a more accurate picture of reality, so that the natural forces of the system can be used to achieve desired results.





















 Talent Assessment
Talent Assessment